

|
Spec-Zone .ru
спецификации, руководства, описания, API
|
| Contents | Prev | Next | JDBCTM Guide: Getting Started |
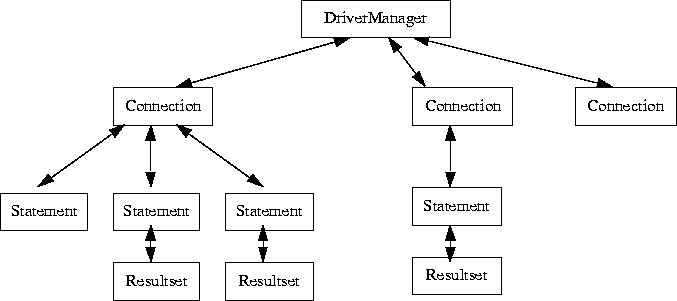
The most important interfaces are:
The following chapters provide more information on how these interfaces work. See the separate JDBC API documents for complete documentation of JDBC interfaces and classes.
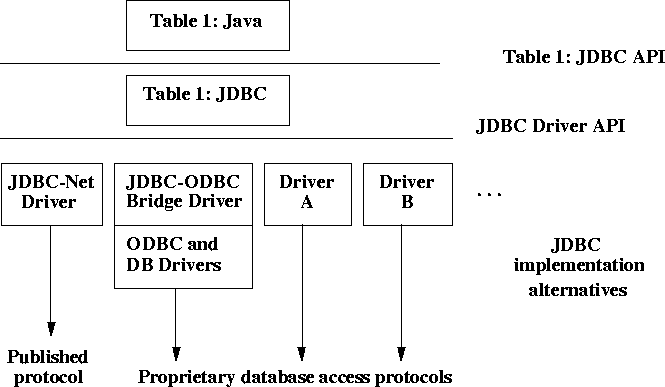
In addition, each database driver needs to provide a class which implements the java.sql.Driver interface used by the generic java.sql.DriverManager class when it needs to locate a driver for a particular database URL.
JavaSoft is providing an implementation of JDBC on top of ODBC, shown as the JDBC-ODBC bridge in the picture. Since JDBC is patterned after ODBC, this implementation is small and efficient.
Another useful driver is one that goes directly to a DBMS-independent network protocol. It would be desirable to publish the protocol to allow multiple server implementations, e.g. on top of ODBC or on specific DBMSs (although there are already products that use a fixed protocol such as this, we are not yet trying to standardize it). Only a few optimizations are needed on the client side, e.g. for schema caching and tuple look-ahead, and the JDBC Manager itself is very small and efficient as well. The net result is a very small and fast all-Java client side implementation that speaks to any server speaking the published protocol.