

|
Spec-Zone .ru
спецификации, руководства, описания, API
|
This section discusses how to perform a rolling restart of a MySQL Cluster installation, so called because it involves stopping and starting (or restarting) each node in turn, so that the cluster itself remains operational. This is often done as part of a rolling upgrade or rolling downgrade, where high availability of the cluster is mandatory and no downtime of the cluster as a whole is permissible. Where we refer to upgrades, the information provided here also generally applies to downgrades as well.
There are a number of reasons why a rolling restart might be desirable. These are described in the next few paragraphs.
Configuration change. To make a change in the cluster's configuration, such as adding an SQL node to the cluster, or setting a configuration parameter to a new value.
MySQL Cluster software upgrade or downgrade. To upgrade the cluster to a newer version of the MySQL Cluster software (or to downgrade it to an older version). This is usually referred to as a "rolling upgrade" (or "rolling downgrade", when reverting to an older version of MySQL Cluster).
Change on node host. To make changes in the hardware or operating system on which one or more MySQL Cluster node processes are running.
System reset (cluster reset). To reset the cluster because it has reached an undesirable state. In such cases it is often desirable to reload the data and metadata of one or more data nodes. This can be done in any of three ways:
Start each data node process (ndbd or possibly ndbmtd) with the --initial option, which forces the data node to clear its file system and
to reload all MySQL Cluster data and metadata from the other data nodes.
Create a backup using the ndb_mgm client BACKUP
command prior to performing the restart. Following the upgrade, restore the node or nodes using ndb_restore.
See Section 17.5.3, "Online Backup of MySQL Cluster", and Section 17.4.18, "ndb_restore — Restore a MySQL Cluster Backup", for more information.
Use mysqldump to create a backup prior to the upgrade;
afterward, restore the dump using LOAD
DATA INFILE.
Resource Recovery. To free memory previously allocated to a
table by successive INSERT and DELETE operations, for re-use by other MySQL Cluster tables.
The process for performing a rolling restart may be generalized as follows:
Stop all cluster management nodes (ndb_mgmd processes), reconfigure them, then restart them. (See Rolling restarts with multiple management servers.)
Stop, reconfigure, then restart each cluster data node (ndbd process) in turn.
Stop, reconfigure, then restart each cluster SQL node (mysqld process) in turn.
The specifics for implementing a given rolling upgrade depend upon the changes being made. A more detailed view of the process is presented here:
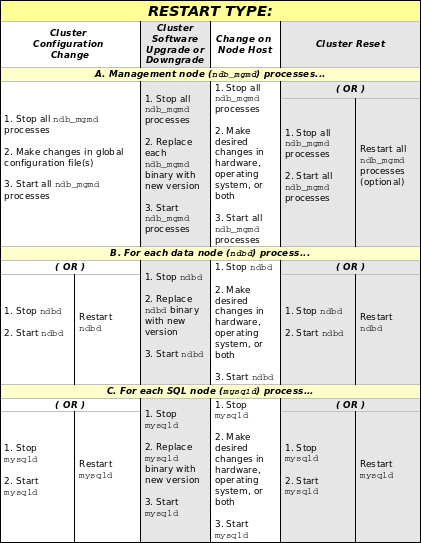
In the previous diagram, the Stop and Start
steps indicate that the process must be stopped completely using a shell command (such as kill on most Unix systems) or the management client STOP command, then started again from a system shell by invoking the ndbd or ndb_mgmd executable as appropriate. On Windows, you can also
use the system NET START and NET STOP commands or the
Windows Service Manager to start and stop nodes which have been installed as Windows services (see Section 17.2.3.4, "Installing
MySQL Cluster Processes as Windows Services").
Restart indicates that the process may be restarted using the ndb_mgm
management client RESTART command (see Section
17.5.2, "Commands in the MySQL Cluster Management Client").
MySQL Cluster supports a flexible order for upgrading nodes. When upgrading a MySQL Cluster, you may upgrade API nodes (including SQL nodes) before upgrading the management nodes, data nodes, or both. In other words, you are permitted to upgrade the API and SQL nodes in any order. This is subject to the following provisions:
This functionality is intended for use as part of an online upgrade only. A mix of node binaries from different MySQL Cluster releases is neither intended nor supported for continuous, long-term use in a production setting.
All management nodes must be upgraded before any data nodes are upgraded. This remains true regardless of the order in which you upgrade the cluster's API and SQL nodes.
Features specific to the "new" version must not be used until all management nodes and data nodes have been upgraded.
This also applies to any MySQL Server version change that may apply, in addition to the NDB engine version change, so do not forget to take this into account when planning the upgrade. (This is true for online upgrades of MySQL Cluster in general.)
See also Bug #48528 and Bug #49163.
Rolling restarts with multiple management servers. When performing a rolling restart of a MySQL Cluster with multiple management nodes, you should keep in mind that ndb_mgmd checks to see if any other management node is running, and, if so, tries to use that node's configuration data. To keep this from occurring, and to force ndb_mgmd to reread its configuration file, perform the following steps:
Stop all MySQL Cluster ndb_mgmd processes.
Update all config.ini files.
Start a single ndb_mgmd with --reload, --initial, or both options as desired.
If you started the first ndb_mgmd with the --initial option, you must also start any remaining ndb_mgmd processes using --initial.
Regardless of any other options used when starting the first ndb_mgmd, you should not start any remaining ndb_mgmd processes after the first one using --reload.
Complete the rolling restarts of the data nodes and API nodes as normal.
When performing a rolling restart to update the cluster's configuration, you can use the config_generation
column of the ndbinfo.nodes
table to keep track of which data nodes have been successfully restarted with the new configuration. See Section 17.5.10.13, "The ndbinfo
nodes Table".